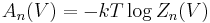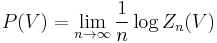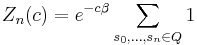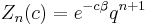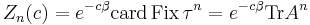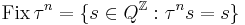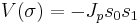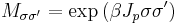Potts model
In statistical mechanics, the Potts model, a generalization of the Ising model, is a model of interacting spins on a crystalline lattice. By studying the Potts model, one may gain insight into the behaviour of ferromagnets and certain other phenomena of solid state physics. The strength of the Potts model is not so much that it models these physical systems well; it is rather that the one-dimensional case is exactly solvable, and that it has a rich mathematical formulation that has been studied extensively.
The model is named after Renfrey B. Potts who described the model near the end of his 1952 Ph.D. thesis. The model was related to the "planar Potts" or "clock model", which was suggested to him by his advisor Cyril Domb. The Potts model is sometimes known as the Ashkin–Teller model (after Julius Ashkin and Edward Teller), as they considered a four component version in 1943.
The Potts model is related to, and generalized by, several other models, including the XY model, the Heisenberg model and the N-vector model. The infinite-range Potts model is known as the Kac model. When the spins are taken to interact in a non-Abelian manner, the model is related to the flux tube model, which is used to discuss confinement in quantum chromodynamics. Generalizations of the Potts model have also been used to model grain growth in metals and coarsening in foams. A further generalization of these methods by James Glazier and Francois Graner, known as the Cellular Potts model has been used to simulate static and kinetic phenomena in foam and biological morphogenesis.
Contents |
Physical description
The Potts model consists of spins that are placed on a lattice; the lattice is usually taken to be a two-dimensional rectangular Euclidean lattice, but is often generalized to other dimensions or other lattices. Domb originally suggested that the spin take one of q possible values, distributed uniformly about the circle, at angles
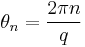 , where
, where 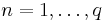
and that the interaction Hamiltonian be given by
with the sum running over the nearest neighbor pairs 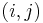 over all lattice sites. The site colors
over all lattice sites. The site colors 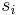 take on values, ranging from
take on values, ranging from  . Here,
. Here, 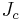 is a coupling constant, determining the interaction strength. This model is now known as the vector Potts model or the clock model. Potts provided a solution for two dimensions, for q=2,3 and 4. In the limit as q approaches infinity, this becomes the XY model.
is a coupling constant, determining the interaction strength. This model is now known as the vector Potts model or the clock model. Potts provided a solution for two dimensions, for q=2,3 and 4. In the limit as q approaches infinity, this becomes the XY model.
What is now known as the standard Potts model was suggested by Potts in the course of the solution above, and uses a simpler Hamiltonian, given by:
where 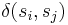 is the Kronecker delta, which equals one whenever
is the Kronecker delta, which equals one whenever 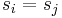 and zero otherwise.
and zero otherwise.
The q=2 standard Potts model is equivalent to the 2D Ising model and the 2-state vector Potts model, with 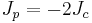 . The q=3 standard Potts model is equivalent to the three-state vector Potts model, with
. The q=3 standard Potts model is equivalent to the three-state vector Potts model, with 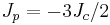 .
.
A common generalization is to introduce an external "magnetic field" term 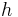 , and moving the parameters inside the sums and allowing them to vary across the model:
, and moving the parameters inside the sums and allowing them to vary across the model:
where 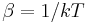 the inverse temperature, k the Boltzmann constant and T the temperature. The summation may run over more distant neighbors on the lattice, or may in fact be an infinite-range force.
the inverse temperature, k the Boltzmann constant and T the temperature. The summation may run over more distant neighbors on the lattice, or may in fact be an infinite-range force.
Different papers may adopt slightly different conventions, which can alter 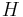 and the associated partition function by additive or multiplicative constants.
and the associated partition function by additive or multiplicative constants.
Discussion
Despite its simplicity as a model of a physical system, the Potts model is useful as a model system for the study of phase transitions. For example, two dimensional lattices with 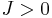 exhibit a first order transition if
exhibit a first order transition if 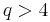 . When
. When 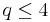 a continuous transition is observed, as in the Ising model where
a continuous transition is observed, as in the Ising model where 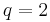 . Further use is found through the model's relation to percolation problems and the Tutte and chromatic polynomials found in combinatorics.
. Further use is found through the model's relation to percolation problems and the Tutte and chromatic polynomials found in combinatorics.
The model has a close relation to the Fortuin-Kasteleyn random cluster model, another model in statistical mechanics. Understanding this relationship has helped develop efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for numerical exploration of the model at small 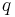 .
.
Measure theoretic description
The one dimensional Potts model may be expressed in terms of a subshift of finite type, and thus gains access to all of the mathematical techniques associated with this formalism. In particular, it can be solved exactly using the techniques of transfer operators. (However, Ernst Ising used combinatorial methods to solve the Ising model, which is the "ancestor" of the Potts model, in his 1925 PhD thesis). This section develops the mathematical formalism, based on measure theory, behind this solution.
While the example below is developed for the one-dimensional case, many of the arguments, and almost all of the notation, generalizes easily to any number of dimensions. Some of the formalism is also broad enough to handle related models, such as the XY model, the Heisenberg model and the N-vector model.
Topology of the space of states
Let 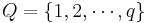 be a finite set of symbols, and let
be a finite set of symbols, and let
be the set of all bi-infinite strings of values from the set Q. This set is called a full shift. For defining the Potts model, either this whole space, or a certain subset of it, a subshift of finite type, may be used. Shifts get this name because there exists a natural operator on this space, the shift operator 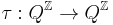 , acting as
, acting as
This set has a natural product topology; the base for this topology are the cylinder sets
that is, the set of all possible strings where k+1 spins match up exactly to a given, specific set of values  . Explicit representations for the cylinder sets can be gotten by noting that the string of values corresponds to a q-adic number, and thus, intuitively, the product topology resembles that of the real number line.
. Explicit representations for the cylinder sets can be gotten by noting that the string of values corresponds to a q-adic number, and thus, intuitively, the product topology resembles that of the real number line.
Interaction energy
The interaction between the spins is then given by a continuous function 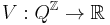 on this topology. Any continuous function will do; for example
on this topology. Any continuous function will do; for example
will be seen to describe the interaction between nearest neighbors. Of course, different functions give different interactions; so a function of 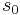 ,
, 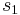 and
and 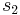 will describe a next-nearest neighbor interaction. A function V gives interaction energy between a set of spins; it is not the Hamiltonian, but is used to build it. The argument to the function V is an element
will describe a next-nearest neighbor interaction. A function V gives interaction energy between a set of spins; it is not the Hamiltonian, but is used to build it. The argument to the function V is an element 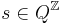 , that is, an infinite string of spins. In the above example, the function V just picked out two spins out of the infinite string: the values
, that is, an infinite string of spins. In the above example, the function V just picked out two spins out of the infinite string: the values 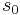 and
and 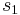 . In general, the function V may depend on some or all of the spins; currently, only those that depend on a finite number are exactly solvable.
. In general, the function V may depend on some or all of the spins; currently, only those that depend on a finite number are exactly solvable.
Define the function 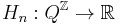 as
as
This function can be seen to consist of two parts: the self-energy of a configuration ![[s_0, s_1, \ldots,s_n]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8603ebb50293e79956d30bd020f36747.png) of spins, plus the interaction energy of this set and all the other spins in the lattice. The
of spins, plus the interaction energy of this set and all the other spins in the lattice. The 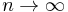 limit of this function is the Hamiltonian of the system; for finite n, these are sometimes called the finite state Hamiltonians.
limit of this function is the Hamiltonian of the system; for finite n, these are sometimes called the finite state Hamiltonians.
Partition function and measure
The corresponding finite-state partition function is given by
with 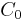 being the cylinder sets defined above. Here, β=1/kT, where k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the temperature. It is very common in mathematical treatments to set β=1, as it is easily regained by rescaling the interaction energy. This partition function is written as a function of the interaction V to emphasize that it is only a function of the interaction, and not of any specific configuration of spins. The partition function, together with the Hamiltonian, are used to define a measure on the Borel σ-algebra in the following way: The measure of a cylinder set, i.e. an element of the base, is given by
being the cylinder sets defined above. Here, β=1/kT, where k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the temperature. It is very common in mathematical treatments to set β=1, as it is easily regained by rescaling the interaction energy. This partition function is written as a function of the interaction V to emphasize that it is only a function of the interaction, and not of any specific configuration of spins. The partition function, together with the Hamiltonian, are used to define a measure on the Borel σ-algebra in the following way: The measure of a cylinder set, i.e. an element of the base, is given by
One can then extend by countable additivity to the full σ-algebra. This measure is a probability measure; it gives the likelihood of a given configuration occurring in the configuration space 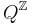 . By endowing the configuration space with a probability measure built from a Hamiltonian in this way, the configuration space turns into a canonical ensemble.
. By endowing the configuration space with a probability measure built from a Hamiltonian in this way, the configuration space turns into a canonical ensemble.
Most thermodynamic properties can be expressed directly in terms of the partition function. Thus, for example, the Helmholtz free energy is given by
Another important related quantity is the topological pressure, defined as
which will show up as the logarithm of the leading eigenvalue of the transfer operator of the solution.
Free field solution
The simplest model is the model where there is no interaction at all, and so 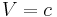 and
and 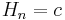 (with
(with 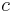 constant and independent of any spin configuration). The partition function becomes
constant and independent of any spin configuration). The partition function becomes
If all states are allowed, that is, the underlying set of states is given by a full shift, then the sum may be trivially evaluated as
If neighboring spins are only allowed in certain specific configurations, then the state space is given by a subshift of finite type. The partition function may then be written as
where card is the cardinality or count of a set, and Fix is the set of fixed points of the iterated shift function:
The 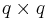 matrix
matrix  is the adjacency matrix specifying which neighboring spin values are allowed.
is the adjacency matrix specifying which neighboring spin values are allowed.
Interacting model
The simplest case of the interacting model is the Ising model, where the spin can only take on one of two values, 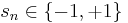 and only nearest neighbor spins interact. The interaction potential is given by
and only nearest neighbor spins interact. The interaction potential is given by
This potential can be captured in a 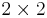 matrix with matrix elements
matrix with matrix elements
with the index 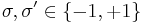 . The partition function is then given by
. The partition function is then given by
The general solution for an arbitrary number of spins, and an arbitrary finite-range interaction, is given by the same general form. In this case, the precise expression for the matrix M is a bit more complex.
The goal of solving a model such as the Potts model is to give the an exact closed-form expression for the partition function (which we've done) and an expression for the Gibbs states or equilibrium states in the limit of 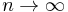 , the thermodynamic limit.
, the thermodynamic limit.
References
- Ashkin, Julius; Teller, Edward (1943). "Statistics of Two-Dimensional Lattices With Four Components". Phys. Rev. 64 (5–6): 178–184. Bibcode 1943PhRv...64..178A. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.64.178.
- Graner, François; Glazier, James A. (1992). "Simulation of Biological Cell Sorting Using a Two-Dimensional Extended Potts Model". Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 (13): 2013–2016. Bibcode 1992PhRvL..69.2013G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.2013.
- Potts, Renfrey B. (1952). "Some Generalized Order-Disorder Transformations". Mathematical Proceedings 48 (1): 106–109. Bibcode 1952PCPS...48..106P. doi:10.1017/S0305004100027419.
- Wu, Fa-Yueh (1982). "The Potts model". Rev. Mod. Phys. 54 (1): 235–268. Bibcode 1982RvMP...54..235W. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.54.235.
External links
- Haggard, Gary; Pearce, David J.; Royle, Gordon. "Code for efficiently computing Tutte, Chromatic and Flow Polynomials". http://www.mcs.vuw.ac.nz/~djp/tutte/.
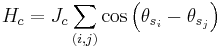
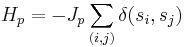
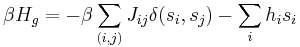
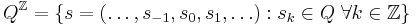
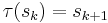
![C_m[\xi_0, \ldots, \xi_k]= \{s \in Q^\mathbb{Z}�:
s_m = \xi_0, \ldots ,s_{m%2Bk} = \xi_k \}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/949f62c9610ae2356708523852e244b5.png)
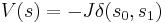
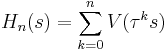
![Z_n(V) = \sum_{s_0,\ldots,s_n \in Q}
\exp(-\beta H_n(C_0[s_0,s_1,\ldots,s_n]))](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/da41136c98b1a2c9c400e4b5d6576f42.png)
![\mu (C_k[s_0,s_1,\ldots,s_n]) =
\frac{1}{Z_n(V)}
\exp(-\beta H_n (C_k[s_0,s_1,\ldots,s_n]))](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/54b74622e62999dbebd4bd11d6e3dcdb.png)